Fighting Cancer with Nutrition
Cancer is a complex disease that results from multiple interactions between genes and the environment. It is regarded as one of the current leading causes of mortality worldwide. Cancer is abnormal division and reproduction of cells that can spread throughout the body. It consists of almost 100 disorders caused by nearly 300 different growths.
Because cancer occurs in cells that are replicating, the patterns of cancer are quite different in children and adults. In early life the brain, nervous system, bones, muscles and connective tissue are still growing. Thus these tissues are more commonly involved with cancerous lesions in children than adults. Conversely, common adult tumors involve epithelial linings. Leukemias and lymphomas, which are cancers of the immune system, occur in both children and adults.
The goals of medical nutrition therapy for patients with cancer are giving the best possible quality of life, controlling cancer related symptoms, maintaining healthy body weight and body strength, keeping body tissue healthy and decreasing side effects before, during and after the treatments.
Cancer and cancer treatments may affect taste, smell, appetite and the ability to eat enough food and absorb nutrients from food. This can cause malnutrition, which is a condition caused by a lack of key nutrients. Malnutrition can cause the patient to be weak, tired, unable to fight infection and complete cancer treatments. Malnutrition may be made worse if the cancer grows or spreads. Medical Nutrition Therapy is important for healing, fighting infection and having enough energy to prevent malnutrition.

Malnutrition associated with cancer patients
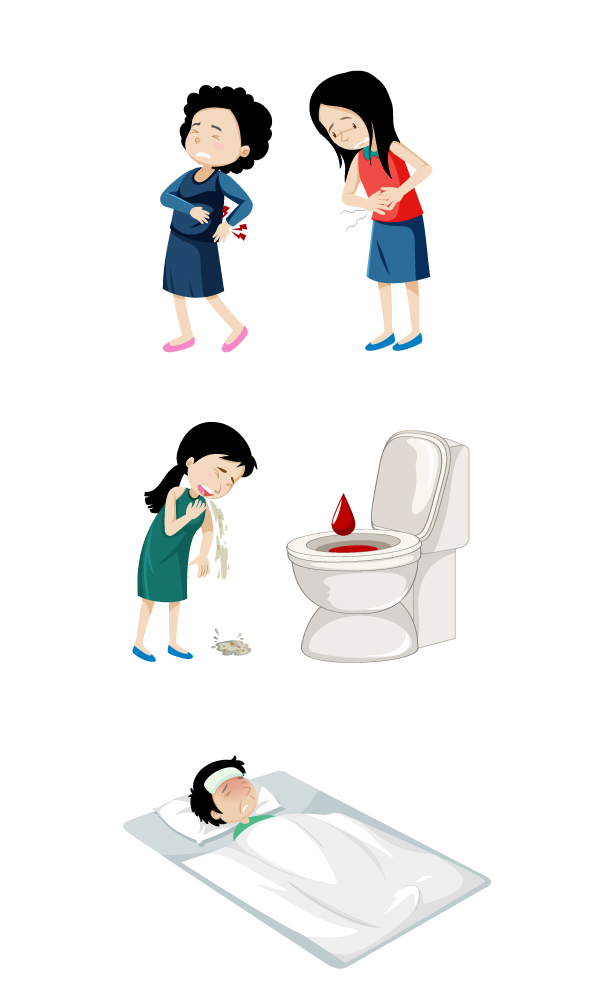
The origin of malnutrition in cancer patients is multi-factorial. The prevalence of malnutrition in cancer patients is higher than in general patients because of cancer-specific characteristics and treatment processes. Most cancer patients undergo surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, immunotherapy and stem cell transplant depending on the type and stage of cancer. These treatments are associated with various side effects. Among these side effects, loss of appetite, sore mouth or throat, dry mouth, change in taste, vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, constipation and fatigue can negatively affect dietary intake.
Malnutrition can cause weakness, tiredness, infection risks, side effects of cancer treatment and mortality rates. Malnutrition may be worse if the cancer grows or spreads. Wasting is accelerated by the proteolysis of skeletal muscle and consumption of body fat. Accelerated mobilization and consumption of host protein stores from peripheral tissues occurs to support gluconeogenesis and acute phase protein synthesis. Consumption of the right amount of protein and calories is important for healing, fighting infection and having enough energy.
Anorexia and cachexia are common causes of malnutrition in cancer patients.
Anorexia is the loss of appetite. It is a common symptom in patients with cancer. Anorexia may occur early in the disease or later, if the cancer grows or spreads. Anorexia may be attributed to altered taste and smell or to changes in the hypothalamic food regulation. Some patients already have anorexia when they are diagnosed with cancer. Most patients who have advanced cancer will have anorexia. Anorexia is the most common cause of malnutrition in cancer patients.
Cachexia is a condition marked by weakness, weight loss, fat loss and muscle loss. It is common in patients with tumors that affect eating and digestion. It can occur in cancer patients who are eating well, but are not storing fat and muscle because of tumor growth. Some tumors change the way the body uses certain nutrients. The body’s use of protein, carbohydrates and fat may be affected, especially by tumors of the stomach, intestines, head and neck. A patient may seem to be eating enough, but the body may not be able to absorb all the nutrients from the food. Disturbance of digestion and absorption also accompanies some tumors. Nutritional demand in the tumor-bearing state is increased due to alterations either by the neoplasm itself or by the stressed host.
Dietary management for cancer
It is important to maintain proper nutrition before, during and after cancer treatments like radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, immunotherapy and surgery. These procedures and medications can cause many individuals to lose their appetite and energy, putting them at an increased risk for malnutrition. On the other hand, some cancer treatments may cause weight gain. The main goal of medical nutrition therapy is to keep body weight constant.
Early nutrition screening and assessment help to find problems that may affect how well the patient’s body deals with the effects of cancer treatment. Finding and treating nutrition problems early can help the patient to gain weight or prevent weight loss, decrease problems with the treatment and help recovery.
It is important to treat cancer symptoms and side effects that affect eating and weight loss early. Strategies for preventing weight loss can be identified as increasing appetite, helping food digestion, treating nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, preventing pain, treating mouth problems such as dry mouth, infection, pain and sores.
In order to minimize weight changes, heal properly and maintain the energy to cope with all the new challenges, a wide variety of high-calorie and high-protein foods need to be incorporated in patient management. Protein helps to ensure growth, repair body tissue and maintain a healthy immune system. Without enough protein, the body takes longer to recover from illness and will have a lower resistance to infection. People with cancer often need more protein than usual.
Nutrition needs are different for patients with advanced cancer. It is common that patients with advanced cancer want less food. Patients usually prefer soft foods and clear liquids. Those who have problems swallowing may do better with thick liquids than with thin liquids. Patients often do not feel much hunger at all and may need very little food.
In patients with advanced cancer, most foods are allowed. During this time, eating can be focused on pleasure rather than getting enough nutrients. Patients usually cannot eat enough of any food that might cause a problem. However, some patients may need to stay on a special diet. For example, patients with cancer that affects the abdomen may need a soft diet to keep the bowel from getting blocked.

Nutrition support for patients with cancer
It is acceptable to take in food by mouth whenever possible. Some patients may not be able to take in enough food by mouth because of problems from cancer or cancer treatment.
A patient who is not able to take in enough food by mouth may be fed using enteral nutrition (through a tube inserted into the stomach or intestines) or parenteral nutrition (infused into the bloodstream). The nutrients are given in liquid formulas that have water, protein, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals.
Nutrition support can improve a patient’s quality of life during cancer treatment, but there are harms that should be considered before making the decision to use it. The patient and health care providers should discuss the harms and benefits of each type of nutrition support prior to implementation.
Enteral Nutrition
Enteral nutrition is giving the patients nutrients in liquid form (formula) through a tube that is placed into the stomach or small intestine.
A nasogastric tube is inserted through the nose and down the throat into the stomach or small intestine. This kind of tube is used when enteral nutrition is only needed for a few weeks. A gastrostomy tube is inserted into the stomach and jejunostomy tube is inserted into the small intestine through an opening made on the outside of the abdomen. This kind of tube is usually used for long-term enteral feeding or for patients who cannot use a tube in the nose and throat.
The type of formula used is based on the specific needs of the patient. There are formulas for patients who have special health conditions such as diabetes, chronic kidney diseases and other chronic conditions.
Enteral nutrition is sometimes used when the patient is able to eat small amounts by mouth, but cannot eat enough for health. Calories and nutrients are given to the patient through tube feeding.
Enteral nutrition may continue even after the patient leaves the hospital. If Enteral nutrition is to be part of the patient’s care after leaving the hospital, the patient and caregiver will be trained to do the nutrition support care at home.
Parenteral Nutrition
Parenteral nutrition is used when the patient can’t take food by mouth or by enteral feeding. Parenteral feeding does not use the stomach or intestines to digest food. Nutrients are given to the patient directly into the blood, through a catheter (thin tube) inserted into a vein. These nutrients include proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. Parenteral nutrition is used only in patients who need nutrition support for five days or more.
If parenteral nutrition is to be part of the patient’s care after leaving the hospital, the patient and caregiver will be trained to do the nutrition support care at home.
Going off parenteral nutrition support needs to be done slowly. It should be supervised by a medical team. The parenteral feedings are decreased by small amounts over time until they can be stopped, or as the patient is changed over to enteral or oral feeding.
Potential side effects & coping strategies
Cancer and associated treatments often result in taste alterations. Chemotherapy can result in the reduced ability to taste sweetness and a higher sensitivity to bitterness. This changes the flavor of foods like sweets, desserts, fruits and vegetables. Some individuals may experience an unusual dislike for certain foods, flavors and odors. Some studies indicate that zinc supplementation may protect against taste disorders.
Pain medications, changes in eating habits and decreased physical activity can cause bowels to move less frequently and stools to pass more difficult leading to constipation. Cancer treatments and medications can cause bowels to move much more frequently and stools to become very loose resulting in diarrhea.
Overall, these side effects can result in decreased calorie intake and not meeting daily energy and nutrient requirements, causing weight loss. In addition to effects on appetite and body weight, psychological well-being can also be affected. The pleasure associated with eating can be negatively impacted, resulting in social and emotional impacts. Taking steps to improve nutrition and eating experience can improve physical and emotional well-being.
The potential side effects and associated coping strategies to be implemented for cancer patients are as follows.
Weight Loss
- Nutrient dense foods & snacks frequently
- Small frequent meals throughout the day
- High calorie high protein foods & snacks
Nausea/vomiting
- Slow eating
- Small frequent meals instead of large meals
- Avoid tight clothing
- Drink beverages before meals instead of with meals
- Eat dry & salty foods (toast, crackers, corn chips)
- Avoid high fat, spicy & highly sweetened foods
- Avoid foods with strong odors
- Eat bland & soft foods in treatment days
- Drink liquids to stay hydrated
- Sit up or keep head raised for at least 1 hour after eating
Constipation
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Foods high in fiber (raw fruits & vegetables, whole grains, legumes)
- Incorporate light/moderate physical activity daily
Sore throat/mouth
- Soft & moist foods
- Avoid dry & rough foods
- Avoid tart, acidic, or salty foods and drinks
- Avoid irritating spices such as chili powder, cloves & hot sauces
- Avoid season foods with herbs
- Consume food at a soothing temperature
- Avoid alcohol, caffeine & tobacco
Diarrhea
- Drink plenty of clear, non-carbonated beverages
- Avoid fried, spicy & highly sweetened foods
- Eat easily digestible foods (apple sauce, banana, yogurt & rice)
- Avoid foods high in fiber, slowly resuming these foods when diarrhea is controlled
- Eat salty snacks
- Take high-potassium foods (fruit juices, potatoes, bananas)
- Avoid foods causing gas/cramping (beans, cabbage, broccoli, spicy foods, carbonated beverages
- Limit milk and other lactose-containing foods
- Avoid chewing gums, sugar-free gums and all candies made with sorbitol
Fatigue
- Nutrient dense foods
- Small frequent meals
- Drink adequate fluids throughout the day
- Moderate physical activity
Dry mouth
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Use broths, soups, gravies & yogurt to moisten foods
- Limit caffeine intake
- Take a swallow of beverage with each bite of food
- Suck on hard candies/ chew gum to stimulate saliva production
Taste changes
- Add extra seasoning/condiments
- New recipes
- Maintain good oral hygiene to help foods taste better
- If metallic taste is present, replace metal silverware with plastic
- Emphasize texture in meals
Poor appetite
- Add lemon/lime juice to foods due to increased preference for tart flavors
- Drink tart beverages (Lemon, lime, cranberry)
- Eat during best times, when feeling hungry
- Small frequent meals
- If liquids are more tolerable than solids, consume nutritionally adequate, high calorie liquids
- Avoid too many liquids with meals to prevent feeling full early
- Nutrient dense food consumption
- Be physically active, serving as an appetite stimulant
- Eat in a pleasant environment
Difficulty in swallowing/ chewing
- Soft, moist, blended foods
- Semi solid foods
- Altered foods & drinks
- Drink with a straw
- Add sauces/liquids to help swallow

Nutrition for cancer survivors
Cancer survivors have special health needs, especially because of the risks of late effects and the cancer coming back. Studies have shown that a healthy diet helps to prevent late effects such as obesity, heart disease and metabolic syndrome. Researchers are studying whether certain diet and exercise habits in cancer survivors can keep cancer from coming back or keep new cancers from forming.
Healthy diet and lifestyle habits can improve the quality of life for cancer survivors. Surveys show that many cancer survivors do not follow cancer prevention guidelines and have lifestyle behaviors that may increase their risk for late effects or make late effects worse. Education programs can help cancer survivors learn how to make behavior changes that keep them healthier. Programs that cover diet, exercise, and stress management are more likely to help cancer survivors make lasting changes.
Plant foods like whole grains, vegetables, fruits, nuts and seeds have antioxidants and phytochemicals that can prevent cancer. They are rich in dietary fiber, vitamins, minerals and phytonutrients. These foods are also naturally low in calories and help to maintain a healthy weight. Antioxidants include vitamin A, C, E, selenium, zinc and some enzymes that absorb and attach to free radicals, preventing them from attacking normal cells and interrupting cancer formation. Consumption of a variety of fruits and vegetables, which are good sources of antioxidants, is a healthy way to get antioxidants in the diet and prevent cancer recurrence in cancer survivors.
Article by
W.T.Nilakshi Madhushani
Dietitian/Clinical Nutritionist
SLMC Reg No-45/128
Sources
- Cleveland Clinic
Similar Articles...

How to Keep Work Stress from Taking Over Your Life
How to Keep Work Stress from Taking Over Your Life In today’s fast-paced and competitive world, work stress has become an all-too-common problem that affects

Hypertension: Everything You Need to Know
Hypertension: Everything You Need to Know Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a chronic medical condition that affects a significant portion of the

Understanding Borderline Personality Disorder: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Understanding Borderline Personality Disorder: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment. Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) is a mental health disorder characterised by instability in mood, behaviour, and relationships.